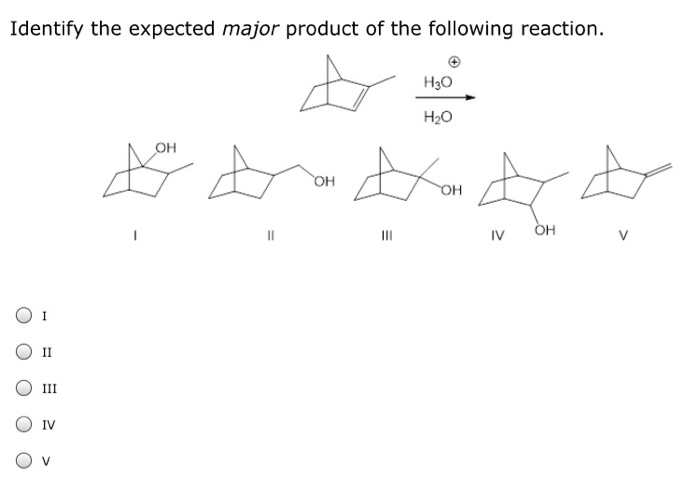
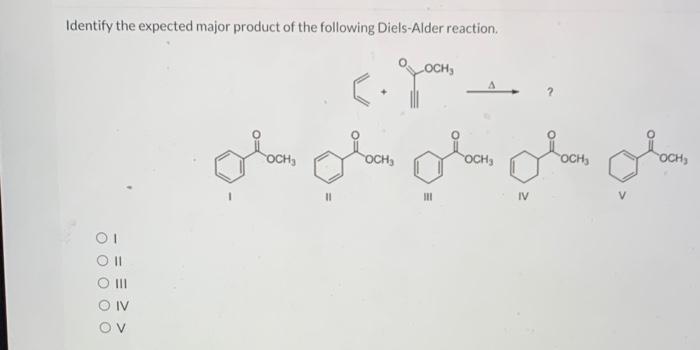
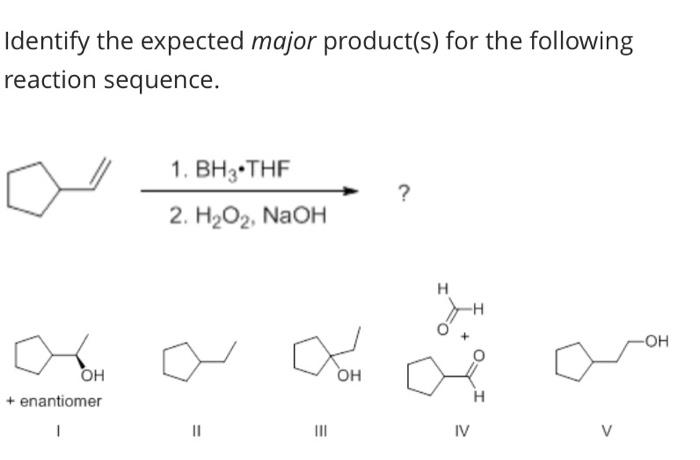
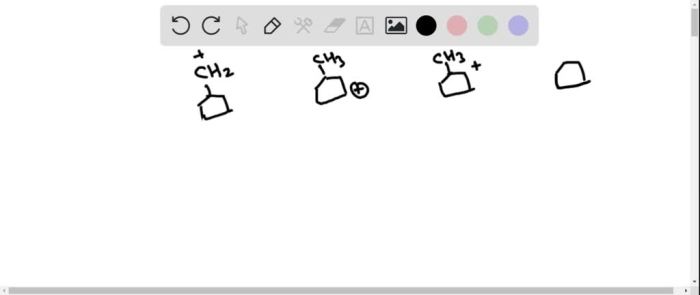
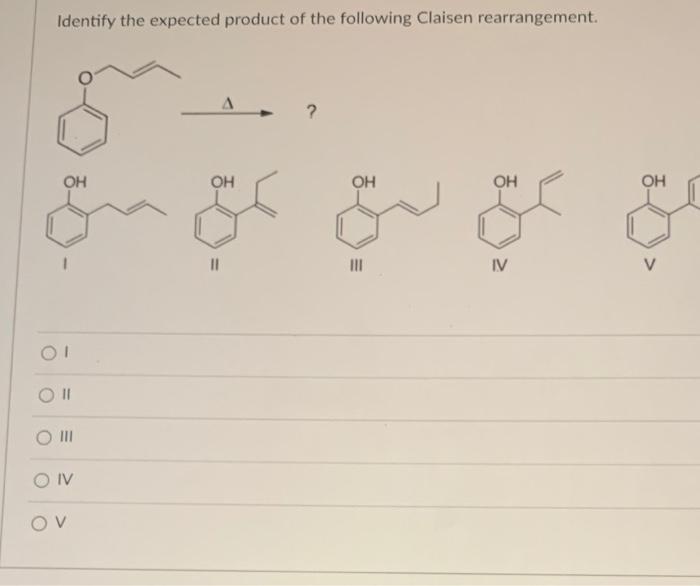
Identify the expected product of the following claisen rearrangement – The Claisen rearrangement is a powerful carbon-carbon bond-forming reaction that involves the rearrangement of an allyl vinyl ether to form a γ,δ-unsaturated carbonyl compound. This reaction is widely used in organic synthesis for the construction of various cyclic and acyclic compounds.
In this article, we will delve into the details of the Claisen rearrangement, including the starting materials, reaction mechanism, regio- and stereoselectivity, and synthetic applications. We will also provide examples to illustrate the versatility of this reaction.
Claisen Rearrangement: Identify The Expected Product Of The Following Claisen Rearrangement
The Claisen rearrangement is a versatile organic reaction that involves the conversion of an allyl vinyl ether into a γ,δ-unsaturated carbonyl compound. This reaction is widely used in organic synthesis for the construction of various carbon-carbon bonds.
Identify the Starting Material
The starting material for the Claisen rearrangement is an allyl vinyl ether, which consists of an allyl group (CH 2=CH-CH 2-) attached to a vinyl ether group (-CH=CH-O-). The allyl group provides the necessary unsaturation for the rearrangement, while the vinyl ether group acts as the leaving group.
Describe the Reaction Mechanism
The Claisen rearrangement proceeds through a concerted pericyclic mechanism involving a [3,3]-sigmatropic shift. The reaction is initiated by the deprotonation of the allyl vinyl ether by a strong base, such as potassium tert-butoxide (t-BuOK). This generates an allyl vinyl anion, which undergoes a 1,3-sigmatropic shift to form a new carbon-carbon bond.
The leaving group (vinyl ether) is expelled during this process, resulting in the formation of a γ,δ-unsaturated carbonyl compound.
Identify the Expected Product, Identify the expected product of the following claisen rearrangement
The expected product of the Claisen rearrangement is a γ,δ-unsaturated carbonyl compound. The regioselectivity of the reaction is determined by the substitution pattern of the allyl group. If the allyl group is substituted, the rearrangement will occur to form the more substituted alkene.
The stereoselectivity of the reaction is typically not high, and a mixture of E and Z isomers is usually obtained.
Provide Examples
Numerous examples of Claisen rearrangements exist, each with its own unique starting material and product. Some common examples include:
- *Allyl phenyl ether rearranges to give cinnamaldehyde
- *Allyl methyl ether rearranges to give crotonaldehyde
- *Allyl acetate rearranges to give 4-penten-2-one
Discuss Applications
The Claisen rearrangement is a powerful synthetic tool that is used in the preparation of a wide range of organic compounds. Some of the applications of the Claisen rearrangement include:
- *Synthesis of unsaturated aldehydes and ketones
- *Construction of cyclic compounds
- *Preparation of natural products
The Claisen rearrangement is a versatile and widely used reaction in organic chemistry, providing a convenient method for the formation of carbon-carbon bonds and the synthesis of various organic compounds.
FAQ Resource
What is the starting material for the Claisen rearrangement?
The starting material for the Claisen rearrangement is an allyl vinyl ether.
What is the product of the Claisen rearrangement?
The product of the Claisen rearrangement is a γ,δ-unsaturated carbonyl compound.
What is the mechanism of the Claisen rearrangement?
The Claisen rearrangement proceeds via a concerted [3,3]-sigmatropic rearrangement.
What are the factors that influence the regio- and stereoselectivity of the Claisen rearrangement?
The regio- and stereoselectivity of the Claisen rearrangement are influenced by the substitution pattern of the allyl vinyl ether, the nature of the base, and the reaction conditions.