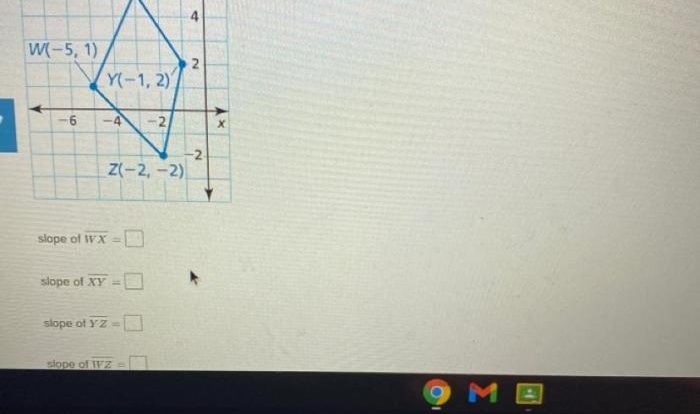
The rigid or nonrigid transformations answer key provides a comprehensive understanding of the fundamental concepts, characteristics, and applications of rigid and nonrigid transformations in geometry. This detailed guide offers a thorough exploration of these transformations, empowering readers with a profound knowledge of their significance in various fields.
Delving into the intricacies of rigid transformations, we uncover their preservation of shape and size, while nonrigid transformations reveal their ability to alter shapes and sizes. This answer key presents a comparative analysis, highlighting the similarities and differences between these two types of transformations.
Rigid Transformations: Rigid Or Nonrigid Transformations Answer Key
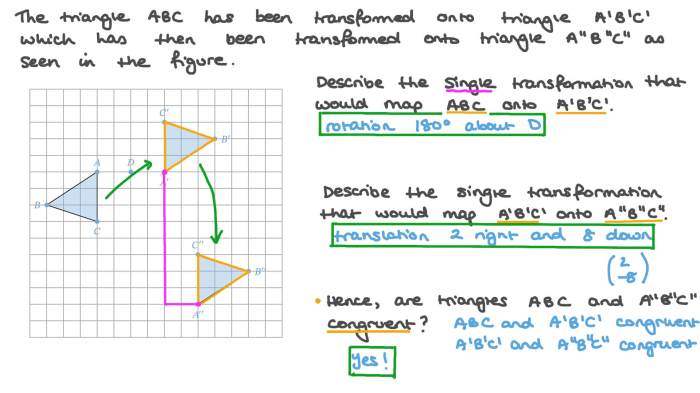
Rigid transformations are transformations that preserve the distance between any two points in a shape. In other words, they do not stretch, shrink, or distort the shape.
Rigid transformations include translations, rotations, and reflections. Translations move a shape from one place to another without changing its orientation. Rotations turn a shape around a fixed point. Reflections flip a shape over a line.
Examples of Rigid Transformations, Rigid or nonrigid transformations answer key
- Moving a shape up, down, left, or right
- Rotating a shape around a fixed point
- Reflecting a shape over a line
| Type of Transformation | Effect on Shape |
|---|---|
| Translation | Moves the shape from one place to another without changing its orientation |
| Rotation | Turns the shape around a fixed point |
| Reflection | Flips the shape over a line |
Nonrigid Transformations
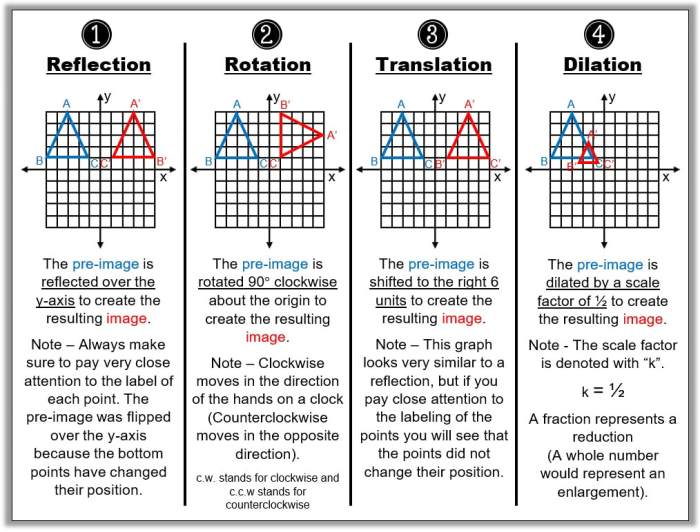
Nonrigid transformations are transformations that do not preserve the distance between any two points in a shape. In other words, they stretch, shrink, or distort the shape.
Nonrigid transformations include dilations, shears, and projections. Dilations enlarge or shrink a shape by a certain factor. Shears tilt a shape in a particular direction. Projections map a shape onto a plane.
Examples of Nonrigid Transformations
- Enlarging or shrinking a shape
- Tilting a shape
- Projecting a shape onto a plane
| Type of Transformation | Effect on Shape |
|---|---|
| Dilation | Enlarges or shrinks a shape by a certain factor |
| Shear | Tilts a shape in a particular direction |
| Projection | Maps a shape onto a plane |
Comparison of Rigid and Nonrigid Transformations
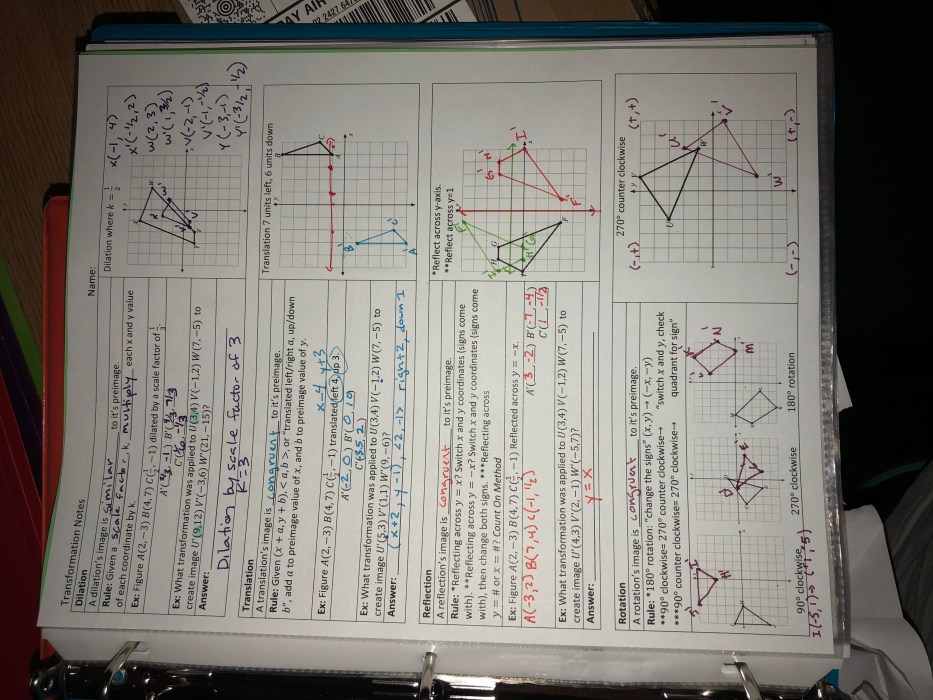
Rigid transformations preserve the distance between any two points in a shape, while nonrigid transformations do not. Rigid transformations include translations, rotations, and reflections, while nonrigid transformations include dilations, shears, and projections.
Rigid transformations are often used in geometry to describe the motion of shapes, while nonrigid transformations are often used in computer graphics to create special effects.
FAQ Section
What are the key characteristics of rigid transformations?
Rigid transformations preserve the shape and size of a figure, meaning that the figure’s angles and side lengths remain unchanged.
How do nonrigid transformations differ from rigid transformations?
Nonrigid transformations alter the shape and/or size of a figure, resulting in a new figure with different angles and/or side lengths.
What are some examples of rigid transformations?
Examples of rigid transformations include translations, rotations, and reflections.
What are some examples of nonrigid transformations?
Examples of nonrigid transformations include dilations, shears, and bends.