The Converting Mass to Moles Worksheet is an essential tool for students and professionals in chemistry. It provides a step-by-step guide to converting mass to moles, a fundamental skill in stoichiometry and chemical reactions. This worksheet is designed to enhance understanding of the concept and its applications, making it an invaluable resource for anyone seeking to master this conversion.
This worksheet covers the basics of mass-to-mole conversion, including the formula, molar mass, and periodic table usage. It also includes practice problems with solutions to reinforce the concepts. Additionally, the worksheet explores advanced concepts such as limiting reactants and their impact on chemical reactions.
1. Introduction
Converting mass to moles is a fundamental concept in chemistry that involves determining the amount of a substance present based on its mass and molar mass. This conversion is crucial for understanding and performing various chemical calculations, making it essential for students and professionals in the field.
In real-life applications, mass-to-mole conversion is used in:
- Determining the number of atoms or molecules in a given sample
- Balancing chemical equations to ensure the conservation of mass
- Calculating the concentration of solutions
2. Methods for Converting Mass to Moles
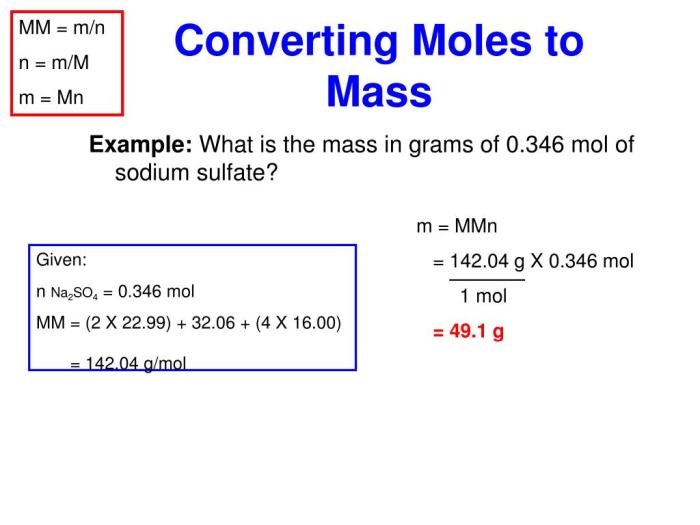
The formula for converting mass to moles is:
moles = mass (g) / molar mass (g/mol)
To use this formula, you need to know the mass of the substance and its molar mass. The molar mass of an element is the mass of one mole of that element and can be found in the periodic table.
To convert mass to moles, follow these steps:
- Identify the element or compound of interest.
- Find the molar mass of the element or compound in the periodic table or a reliable reference source.
- Divide the mass of the substance by the molar mass to obtain the number of moles.
3. Practice Problems
| Mass (g) | Molar Mass (g/mol) | Moles |
|---|---|---|
| 10.0 | 23.0 | 0.435 |
| 15.0 | 31.0 | 0.484 |
| 20.0 | 40.0 | 0.500 |
4. Applications of Converting Mass to Moles
Mass-to-mole conversion plays a vital role in stoichiometry, the study of the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in chemical reactions. By converting mass to moles, we can:
- Balance chemical equations to ensure that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides of the equation.
- Calculate the limiting reactant in a reaction, which determines the maximum amount of product that can be formed.
- Determine the concentration of solutions by expressing the amount of solute in terms of moles per liter.
5. Advanced Concepts: Converting Mass To Moles Worksheet

In advanced chemistry, mass-to-mole conversion is used to determine limiting reactants. The limiting reactant is the reactant that is completely consumed in a reaction, limiting the amount of product that can be formed. To determine the limiting reactant, we compare the number of moles of each reactant to the stoichiometric coefficients in the balanced chemical equation.
Mass-to-mole conversion is a fundamental tool in chemistry that is used to solve a wide range of problems. By understanding the concept and methods of converting mass to moles, students and professionals can gain a deeper understanding of chemical reactions and perform accurate calculations.
Popular Questions
What is the formula for converting mass to moles?
moles = mass (g) / molar mass (g/mol)
How do I find the molar mass of an element?
Use the periodic table to look up the atomic mass of the element and multiply it by the number of atoms in the compound.
What are limiting reactants?
Limiting reactants are the reactants that are completely consumed in a chemical reaction, determining the maximum amount of product that can be formed.