Quiz 2-1 characteristics of functions part 1 answer key – Embark on an enlightening journey with Quiz 2-1: Characteristics of Functions Part 1 Answer Key. This comprehensive guide unlocks the intricacies of functions, empowering you to decipher their defining traits, explore their diverse types, and unravel their practical applications.
Delve into the fundamental concepts of functions, unraveling their domain and range, and gaining insights into their distinct behaviors. Discover the nuances of linear, quadratic, and exponential functions, and witness how these mathematical building blocks shape our understanding of the world around us.
1. Quiz Introduction
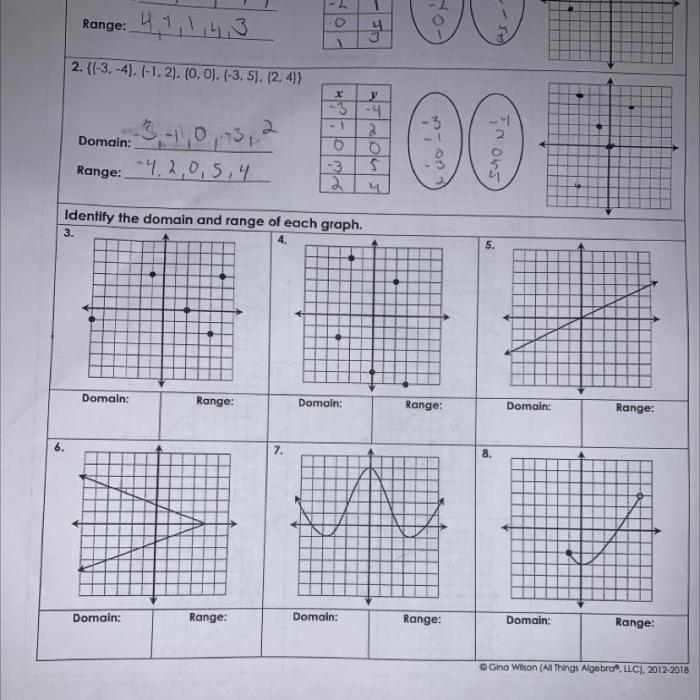
This quiz assesses your understanding of the characteristics of functions. It covers the basic concepts, types, and operations related to functions.
The quiz consists of multiple-choice questions and short answer questions. Please answer all questions to the best of your ability.
2. Characteristics of Functions
A function is a relation that assigns to each element of a set a unique element of another set. The set of elements to which the function is applied is called the domain, and the set of elements that the function produces is called the range.
Functions can be classified into different types, such as linear, quadratic, and exponential. Linear functions are functions whose graphs are straight lines. Quadratic functions are functions whose graphs are parabolas. Exponential functions are functions whose graphs are curves that increase or decrease rapidly.
3. Function Operations: Quiz 2-1 Characteristics Of Functions Part 1 Answer Key
Functions can be combined using a variety of operations, including addition, subtraction, multiplication, and composition.
The sum of two functions f and g, denoted f + g, is a function whose value at any given input is the sum of the values of f and g at that input.
The difference of two functions f and g, denoted f – g, is a function whose value at any given input is the difference of the values of f and g at that input.
The product of two functions f and g, denoted f – g, is a function whose value at any given input is the product of the values of f and g at that input.
The composition of two functions f and g, denoted f o g, is a function whose value at any given input is the value of f evaluated at the output of g.
4. Graphing Functions
Functions can be graphed using tables and equations.
A table of values for a function lists the input values and the corresponding output values.
An equation of a function is an algebraic expression that represents the relationship between the input and output values.
The graph of a function is a visual representation of the relationship between the input and output values.
5. Applications of Functions
Functions are used in a wide variety of fields, including science, engineering, and economics.
In science, functions are used to model the behavior of physical systems. For example, the function y = f(x) = x^2 models the trajectory of a projectile.
In engineering, functions are used to design and analyze structures and systems. For example, the function y = f(x) = x^3 models the bending moment in a beam.
In economics, functions are used to model the behavior of markets and economies. For example, the function y = f(x) = x^2 models the demand for a product.
Helpful Answers
What is the purpose of Quiz 2-1?
Quiz 2-1 is designed to assess your understanding of the fundamental characteristics of functions, including their domain, range, and various types.
How is the quiz structured?
The quiz consists of multiple-choice questions that cover a range of topics related to functions, including their properties, operations, and applications.
What is the difficulty level of the quiz?
The quiz is designed to be accessible to students with a basic understanding of functions. However, some questions may require more in-depth knowledge of the subject.

