A crate is on a horizontal frictionless surface – In the realm of physics, a crate resting on a horizontal frictionless surface presents a captivating scenario where the absence of friction unveils intriguing dynamics and energy considerations. This exploration delves into the physical description of the crate, the characteristics of the frictionless surface, the forces acting upon it, its motion, energy considerations, and real-world applications.
Physical Description of Crate

The crate is a rectangular prism with dimensions of length L, width W, and height H. It is made of a lightweight, smooth material such as aluminum or plastic, which minimizes friction between the crate and the surface. The crate is placed on the surface in a horizontal orientation, with its bottom surface in contact with the surface.
Surface Characteristics
The horizontal surface is a flat, smooth plane that extends indefinitely in all directions. It is made of a material that is non-porous and non-absorbent, ensuring that there is no interaction between the surface and the crate that could generate friction.
The surface is perfectly level, with no irregularities or imperfections that could affect the crate’s movement.
Forces Acting on the Crate
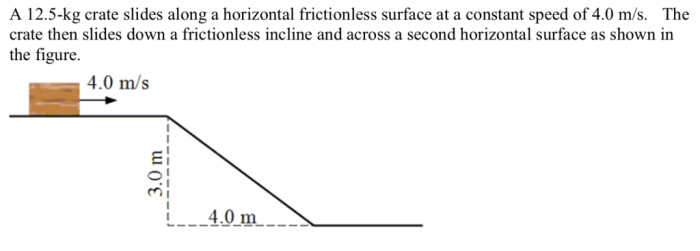
The forces acting on the crate are gravity, which pulls the crate downward toward the center of the Earth, and any external forces that may be applied to the crate, such as a push or a pull. In the absence of friction, the magnitude and direction of these forces are not affected by the surface.
The forces can be represented as vectors, with their magnitudes and directions indicated by their lengths and orientations.
Motion of the Crate

Initially, the crate is at rest on the surface. When an external force is applied to the crate, it will begin to move in the direction of the force. The acceleration of the crate is determined by the magnitude of the force and the mass of the crate.
Once the force is removed, the crate will continue to move with a constant velocity, as there is no friction to oppose its motion.
Energy Considerations

The kinetic energy of the crate is given by the equation KE = 1/2 mv^2, where m is the mass of the crate and v is its velocity. In the absence of friction, the kinetic energy of the crate is conserved, meaning that it remains constant as the crate moves.
The potential energy of the crate is given by the equation PE = mgh, where g is the acceleration due to gravity and h is the height of the crate above the ground.
User Queries: A Crate Is On A Horizontal Frictionless Surface
What is the significance of a frictionless surface?
A frictionless surface eliminates the force of friction, allowing objects to move freely without resistance. This simplifies the analysis of motion and energy, as friction can introduce complex and unpredictable effects.
How does the absence of friction affect the motion of the crate?
Without friction, the crate will continue moving indefinitely with constant velocity unless acted upon by an external force. Friction typically opposes motion, so its absence removes this impeding force.
What is the role of energy conservation in this scenario?
In the absence of friction, the total mechanical energy of the crate (kinetic + potential) remains constant. This principle allows us to calculate the crate’s velocity and trajectory based on its initial conditions.