Navigating the intricacies of ICD-10-PCS coding can be a formidable task. This comprehensive guide, aptly titled “ICD-10-PCS Coding Scenarios with Answers,” is meticulously crafted to unravel the complexities of this coding system, providing a roadmap to accurate and efficient documentation in healthcare.
Within these pages, you will encounter real-world scenarios that mirror the challenges faced by coders, delving into surgical, diagnostic, and therapeutic procedures. Each scenario is meticulously analyzed, revealing the rationale behind the correct ICD-10-PCS code selection, empowering you with the knowledge to confidently navigate the coding landscape.
ICD-10-PCS Coding Scenarios: Icd-10-pcs Coding Scenarios With Answers
Coding scenarios provide practical examples of ICD-10-PCS coding challenges, covering various procedure types and complexities.
Surgical Procedures, Icd-10-pcs coding scenarios with answers
- Scenario: A patient undergoes a laparoscopic cholecystectomy with intraoperative cholangiogram.
- Scenario: A patient has a robotic-assisted total knee replacement.
Diagnostic Procedures
- Scenario: A patient receives a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain with and without contrast.
- Scenario: A patient undergoes a colonoscopy with polypectomy.
Therapeutic Procedures
- Scenario: A patient receives radiation therapy for lung cancer.
- Scenario: A patient undergoes chemotherapy for breast cancer.
Coding Solutions and Rationale

For each scenario, the correct ICD-10-PCS code is provided along with a detailed explanation of the coding rationale.
| Scenario | Code | Description | Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Laparoscopic cholecystectomy with intraoperative cholangiogram | 0B540ZZ | Laparoscopic cholecystectomy with intraoperative cholangiogram | The code includes both the laparoscopic cholecystectomy (0B540) and the intraoperative cholangiogram (ZZ). |
| Robotic-assisted total knee replacement | 0W040ZZ | Total knee replacement, robotic-assisted | The code specifies the use of robotic assistance (ZZ) in the total knee replacement procedure (0W040). |
Common Coding Errors and Prevention
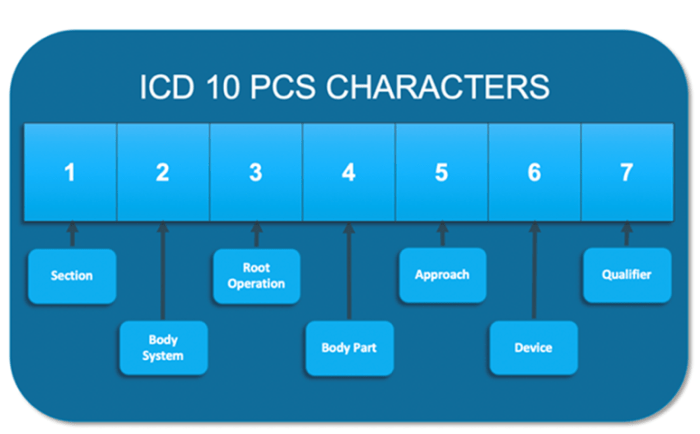
- Error: Using an incorrect code for the laterality of the procedure (e.g., coding a left-sided procedure as right-sided).
- Error: Failing to include all relevant modifiers (e.g., omitting the modifier for a laparoscopic procedure).
- Error: Incorrectly sequencing codes (e.g., coding the primary procedure after a secondary procedure).
Prevention Strategies
- Carefully review the operative report and identify all relevant details.
- Use coding guidelines and references to ensure correct code selection.
- Follow established coding conventions and standards.
Best Practices for Accurate Coding

Accurate ICD-10-PCS coding requires adherence to best practices, including:
- Thorough documentation review
- Careful code selection based on procedure details
- Compliance with coding standards and guidelines
- Staying up-to-date with coding changes
- Utilizing resources for coding assistance (e.g., coding manuals, online databases)
Impact of Accurate Coding
Accurate ICD-10-PCS coding has significant implications for healthcare organizations, including:
- Appropriate reimbursement
- Improved patient care and resource allocation
- Compliance with regulatory requirements
- Enhanced data quality for research and quality improvement
FAQ Overview
What are the key principles of accurate ICD-10-PCS coding?
Accurate ICD-10-PCS coding hinges on meticulous documentation review, precise code selection, and unwavering adherence to coding standards.
How can I prevent common coding errors in ICD-10-PCS?
To avoid common pitfalls, focus on understanding the specific criteria for each code, consulting reliable coding references, and seeking guidance from experienced coders.
What are the implications of inaccurate ICD-10-PCS coding for healthcare organizations?
Inaccurate coding can lead to incorrect reimbursement, compromised patient care, and hindered resource allocation, negatively impacting the overall efficiency of healthcare delivery.