Food chains and webs what’s for dinner – In the intricate tapestry of life, food chains and webs play a pivotal role in shaping the availability of sustenance for diverse species. This article delves into the complexities of these ecological networks, examining their structure, interconnectedness, and the profound influence they exert on ecosystem stability.
Food chains, linear sequences of organisms that transfer energy from producers to consumers, provide a simplified representation of the feeding relationships within an ecosystem. Food webs, on the other hand, capture the intricate interconnections between multiple food chains, revealing the complex dynamics that govern the flow of energy and nutrients.
Food Chains
Food chains depict the linear flow of energy and nutrients through an ecosystem. Each organism in the chain consumes the one below it, transferring energy and matter.
Examples of Food Chains:
- Grass → Grasshopper → Bird → Hawk
- Phytoplankton → Zooplankton → Fish → Shark
Roles in Food Chains:
- Producers:Autotrophic organisms (e.g., plants, algae) that create organic matter through photosynthesis.
- Consumers:Heterotrophic organisms that consume other organisms for energy and nutrients.
- Primary Consumers:Herbivores that eat producers.
- Secondary Consumers:Carnivores that eat primary consumers.
- Tertiary Consumers:Carnivores that eat secondary consumers.
- Decomposers:Organisms (e.g., bacteria, fungi) that break down dead organisms, returning nutrients to the ecosystem.
Food Webs
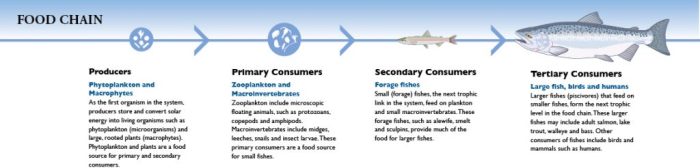
Food webs are complex, interconnected networks of food chains that show the feeding relationships between multiple species in an ecosystem.
Differences from Food Chains:
- Food webs involve multiple interconnected food chains.
- One species can have multiple food sources and be consumed by multiple predators.
Importance for Ecosystem Stability:
- Provide redundancy and resilience to environmental changes.
- Prevent overpopulation of any one species.
- Maintain ecosystem balance and biodiversity.
What’s for Dinner?
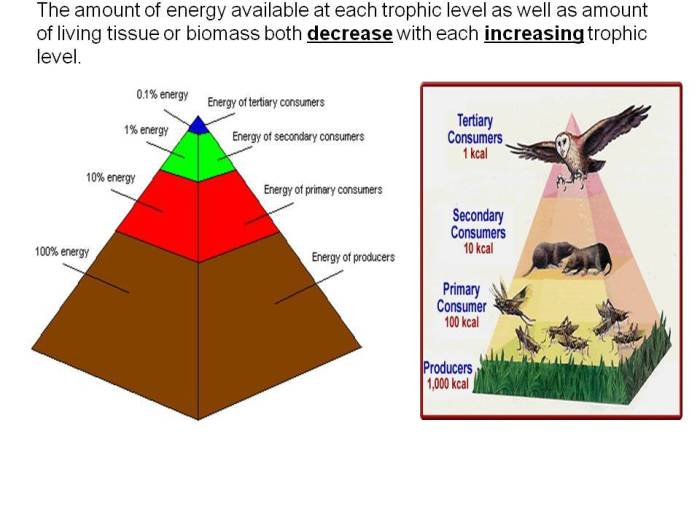
Food chains and webs determine the availability of food for different species, influencing their survival and abundance.
Impact of Human Activities:
- Habitat Destruction:Loss of habitats reduces food sources for species.
- Overfishing:Depletion of fish stocks disrupts food chains and webs.
- Pollution:Toxins can accumulate in organisms, affecting their health and food availability.
Examples of Impacts:
- Decline in prey species can lead to starvation for predators.
- Removal of top predators can result in overpopulation of prey species, damaging ecosystems.
Case Studies: Food Chains And Webs What’s For Dinner
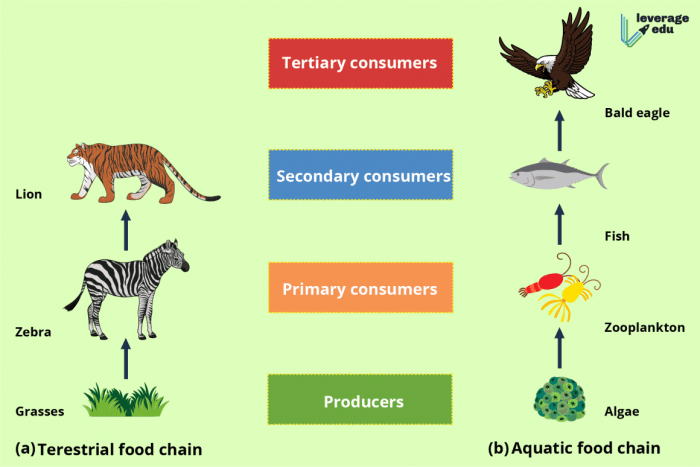
Specific food chains and webs provide insights into their complexity and dynamics.
Example Case Study: Serengeti Food Web
- Interactions between lions, zebras, wildebeest, and vultures.
- Importance of seasonal migrations and water availability.
- Impact of poaching on food web stability.
Implications:
- Highlight the interdependence of species.
- Emphasize the importance of conservation efforts.
Interactive Table
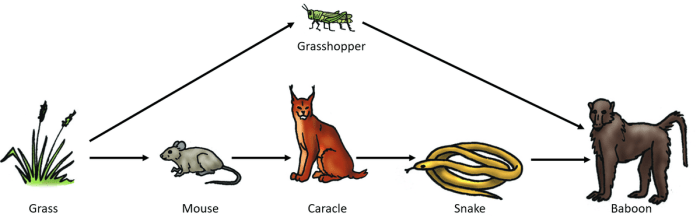
The interactive table provides an interactive way to explore food chains and webs.
Features:
- Species, trophic levels, and interactions.
- Filtering and sorting options.
Benefits:
- Visualization of complex food webs.
- Analysis of species interactions.
- Understanding the role of food chains and webs in ecosystem functioning.
Key Questions Answered
What is the difference between a food chain and a food web?
A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms that transfer energy from producers to consumers, while a food web is a complex network of interconnected food chains that depicts the feeding relationships between multiple species within an ecosystem.
How do food chains and webs influence the availability of food for different species?
Food chains and webs determine the flow of energy and nutrients through an ecosystem, influencing the availability of food resources for different species. Changes in these networks, such as the introduction of invasive species or habitat loss, can have cascading effects on the abundance and distribution of species.
What is the role of decomposers in food chains and webs?
Decomposers, such as bacteria and fungi, play a crucial role in food chains and webs by breaking down dead organisms and organic matter, releasing nutrients back into the ecosystem. This process supports the growth of producers, which form the foundation of food chains.