Embark on a captivating journey with science a to z puzzle answers, your ultimate guide to unraveling the mysteries of the scientific world. Dive into a treasure trove of definitions, experiments, discoveries, and more, all presented in a captivating and accessible manner.
Prepare to quench your thirst for knowledge as we delve into the intricacies of science, from its fundamental principles to its groundbreaking innovations. Get ready to uncover the secrets of the universe and beyond!
Science Terms and Definitions

Science has its own unique vocabulary, consisting of terms and definitions that are essential for understanding scientific concepts. These terms often have specific meanings within the context of science, and it is important to be familiar with them in order to comprehend scientific literature and discussions.This
If you’re stumped by those tricky science A to Z puzzle answers, don’t despair. A quick detour to Macbeth study questions for Act 3 might provide some inspiration. Shakespeare’s insights into human nature can often shed light on the complexities of science, so don’t be afraid to explore the unexpected connections between these seemingly disparate subjects.
After all, returning to the science A to Z puzzle answers with a fresh perspective can often lead to the elusive solutions you seek.
comprehensive list of science terms and definitions covers a wide range of scientific fields, from astronomy to zoology. The terms are organized alphabetically for easy reference, and their etymologies and origins are explained to provide a deeper understanding of their meanings.
Astronomy
- Astronomy: The scientific study of celestial objects (such as stars, planets, galaxies, and nebulae) and the phenomena that originate outside the Earth’s atmosphere.
- Galaxy: A massive, gravitationally bound system of stars, gas, dust, and dark matter.
- Light-year: A unit of distance in astronomy, equal to the distance that light travels in one year (approximately 9.46 trillion kilometers or 5.88 trillion miles).
- Planet: A celestial body that orbits a star, is spherical in shape, and has cleared its orbit of other objects.
- Star: A self-luminous celestial body that generates energy through nuclear fusion in its core.
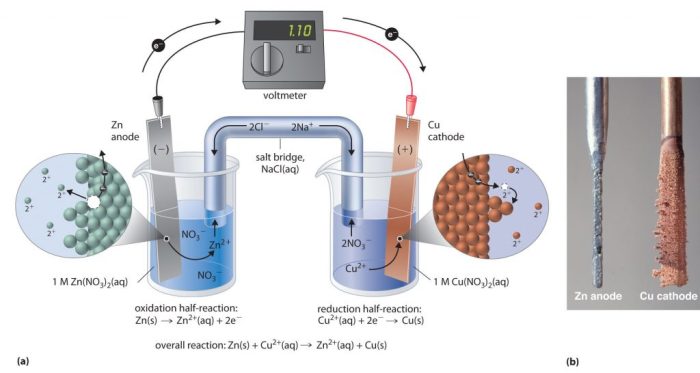
Scientific Experiments and Procedures
Scientific experiments form the backbone of scientific inquiry, enabling us to test hypotheses, explore phenomena, and deepen our understanding of the natural world. These experiments involve carefully designed procedures, specific materials, and controlled conditions to ensure reliable and accurate results.
To effectively conduct scientific experiments, it’s crucial to follow established protocols and adhere to safety guidelines. This ensures the safety of individuals involved and the integrity of the experimental process.
Designing Scientific Experiments
The design of a scientific experiment is paramount to its success. It involves clearly defining the research question, identifying variables, and establishing a hypothesis. The experiment should be designed to control extraneous variables that could potentially confound the results.
The materials used in an experiment should be carefully selected to ensure their suitability for the intended purpose. Proper handling and disposal of materials are also essential considerations to minimize potential hazards.
Conducting Scientific Experiments
Once the experiment is designed, it’s time to conduct it meticulously. This involves following the established procedures step-by-step, recording observations accurately, and analyzing the data objectively.
Safety should always be a top priority during experimentation. Appropriate protective gear, such as gloves, goggles, and lab coats, should be worn when handling hazardous materials or equipment.
Analyzing and Interpreting Results
After conducting the experiment, the data collected needs to be analyzed and interpreted. Statistical methods can be employed to determine the significance of the results and draw meaningful conclusions.
It’s important to consider potential sources of error and limitations of the experiment when interpreting the results. This helps in assessing the reliability and generalizability of the findings.
Science History and Discoveries
Science has been an integral part of human civilization since its inception, shaping our understanding of the world and propelling technological advancements. From the ancient Greeks to modern-day researchers, countless scientists have dedicated their lives to unraveling the mysteries of the universe, making groundbreaking discoveries that have transformed our lives.
Timeline of Significant Scientific Discoveries and Inventions
- 3500 BCE:Invention of the wheel in Mesopotamia
- 1500 BCE:Development of the first calendar in Egypt
- 600 BCE:Thales of Miletus proposes that water is the fundamental element
- 300 BCE:Euclid develops geometry
- 100 CE:Zhang Heng invents the seismoscope
- 1665:Robert Hooke discovers cells
- 1705:Isaac Newton publishes his laws of motion and universal gravitation
- 1803:John Dalton develops the atomic theory
- 1859:Charles Darwin publishes “On the Origin of Species”
- 1869:Dmitri Mendeleev publishes the periodic table
- 1895:Wilhelm Röntgen discovers X-rays
- 1905:Albert Einstein publishes his theory of special relativity
- 1928:Alexander Fleming discovers penicillin
- 1953:James Watson and Francis Crick discover the structure of DNA
- 1969:Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin become the first humans to walk on the moon
- 1989:Tim Berners-Lee invents the World Wide Web
- 2001:Completion of the Human Genome Project
- 2012:Higgs boson discovered at the Large Hadron Collider
Impact of Scientific Advancements on Society and Technology
Scientific discoveries and inventions have had a profound impact on human society and technological progress. They have:
- Improved our understanding of the natural world and our place in it
- Led to the development of new technologies and industries
- Improved healthcare and increased life expectancy
- Shaped our culture and values
- Raised ethical and philosophical questions about the use of science
Anecdotes and Stories about Scientists and Their Struggles and Triumphs
The history of science is filled with stories of brilliant scientists who overcame adversity and made remarkable discoveries. Here are a few examples:
- Marie Curiefaced prejudice as a woman in science but persevered to become the first person to win two Nobel Prizes.
- Albert Einsteinfailed his college entrance exam but went on to revolutionize physics.
- Charles Darwinspent years developing his theory of evolution, despite facing ridicule from his peers.
- Rosalind Franklinplayed a crucial role in the discovery of the structure of DNA, but her contributions were initially overlooked.
These stories remind us that scientific progress is often the result of hard work, perseverance, and the ability to overcome obstacles.
Science Applications and Innovations
Scientific principles have revolutionized various fields, leading to practical applications that enhance our lives. From medical advancements to engineering feats and agricultural innovations, science continues to shape the world we live in.
Medicine
- Diagnostics and Treatment:Scientific advancements have led to the development of sophisticated diagnostic tools and effective treatments for diseases, improving patient outcomes and saving lives.
- Vaccines and Pharmaceuticals:Vaccines have eradicated or controlled deadly diseases, while pharmaceuticals provide relief and management for chronic conditions.
- Medical Imaging:Techniques like X-rays, MRI, and ultrasound allow doctors to visualize internal structures, aiding in diagnosis and treatment planning.
Engineering
- Infrastructure:Scientific principles guide the design and construction of bridges, buildings, and transportation systems, ensuring their safety and efficiency.
- Materials Science:Advances in materials science have led to the development of lightweight, durable, and energy-efficient materials used in various industries.
- Robotics and Automation:Robots and automated systems are transforming manufacturing, healthcare, and other sectors, increasing productivity and precision.
Agriculture
- Crop Improvement:Genetic engineering and selective breeding have resulted in crops with improved yield, resistance to pests and diseases, and nutritional value.
- Fertilizers and Pesticides:Scientific research has led to the development of fertilizers and pesticides that increase crop production while minimizing environmental impact.
- Precision Farming:Technologies like GPS and sensors allow farmers to monitor and manage their fields with greater accuracy, optimizing resource utilization.
Potential Benefits and Limitations of Emerging Scientific Technologies, Science a to z puzzle answers
Emerging scientific technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI), gene editing, and nanotechnology, offer immense potential for advancements in healthcare, energy, and other sectors. However, it’s crucial to consider both their benefits and potential limitations:
- Benefits:Faster drug discovery, personalized medicine, renewable energy sources, and improved materials.
- Limitations:Ethical concerns about gene editing, potential job displacement due to automation, and environmental risks associated with nanotechnology.
Ethical Implications and Societal Impact of Scientific Innovations
Scientific innovations have profound ethical and societal implications that must be carefully considered:
- Equity and Access:Ensuring equitable access to scientific advancements and addressing potential biases in AI and other technologies.
- Privacy and Security:Balancing the benefits of data collection and analysis with the need for privacy and security.
- Public Understanding and Trust:Promoting scientific literacy and fostering public trust in scientific institutions and research.
Science Education and Outreach
Science education aims to provide students with the knowledge and skills to understand the natural world and make informed decisions about science-related issues. It involves a range of teaching methods and strategies to cater to students of all ages and abilities.Hands-on
activities and experiential learning play a crucial role in science education. These activities allow students to engage with scientific concepts through practical experiments, simulations, and real-world experiences. By actively participating in these activities, students develop a deeper understanding of the subject matter and retain information more effectively.
Teaching Methods in Science Education
| Method | Description | Benefits ||—|—|—|| Inquiry-based learning | Students actively engage in the learning process by asking questions, investigating problems, and drawing conclusions. | Promotes critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and scientific literacy. || Project-based learning | Students work on long-term projects that require them to apply scientific concepts to real-world problems.
| Develops teamwork, communication skills, and project management abilities. || Cooperative learning | Students work in small groups to complete tasks and learn from each other. | Enhances collaboration, communication, and peer-to-peer learning. || Technology-enhanced learning | Technology is integrated into the learning process to enhance student engagement and provide access to a wider range of resources.
| Facilitates interactive simulations, virtual labs, and online learning platforms. || Outdoor learning | Students engage in science activities in natural settings, such as field trips and nature walks. | Promotes environmental awareness, observation skills, and appreciation for biodiversity. |
Science Careers and Opportunities: Science A To Z Puzzle Answers
Science offers a wide range of career paths, each with its own unique set of responsibilities and opportunities. Whether you’re interested in conducting research, teaching, or working in industry, there’s a science career that’s right for you.
- Research:Research scientists conduct experiments and collect data to advance our understanding of the natural world. They may work in academia, government, or industry. A PhD is typically required for a research career.
- Academia:Academics teach and conduct research at colleges and universities. They typically have a PhD and may also have experience working in industry or government.
- Industry:Scientists working in industry use their knowledge to develop new products and technologies. They may work in a variety of settings, including manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and energy.
The educational requirements for a science career vary depending on the specific field and position. However, most scientists have at least a bachelor’s degree in science. Some positions may also require a master’s degree or PhD.In addition to education, scientists need a strong foundation in math and problem-solving skills.
They must also be able to communicate their findings effectively to both scientific and non-scientific audiences.If you’re interested in a career in science, there are several things you can do to prepare yourself. First, make sure you have a strong foundation in math and science.
Second, get involved in extracurricular activities that will help you develop your problem-solving skills and communication skills. Finally, network with scientists and professionals in your field of interest.
Science in the News and Media
Science permeates our daily lives, and the news and media play a crucial role in disseminating scientific information to the public. This section explores the significance of science in the news, its accuracy, and the role of science communication in shaping public understanding.
Monitoring Science News
Staying abreast of current science news allows us to identify emerging trends and groundbreaking discoveries. By monitoring news outlets, scientific journals, and reputable online sources, we can gain insights into the latest advancements and their potential impact on society.
Science and Society
Science and society have a complex and multifaceted relationship. Scientific research and innovation are influenced by social and cultural factors, while science also impacts human values and beliefs. Understanding this relationship is crucial for fostering a mutually beneficial relationship between science and society.
Social and cultural factors shape the direction of scientific research and innovation. Societal needs, values, and beliefs can influence which scientific fields receive funding and support. For instance, during times of war, there may be an increased focus on developing new weapons technologies, while in times of peace, there may be a greater emphasis on medical research and environmental protection.
Impact of Science on Human Values and Beliefs
Science has had a profound impact on human values and beliefs. Scientific discoveries have challenged traditional beliefs and led to new understandings of the world. For example, the theory of evolution has changed our understanding of human origins and our place in the natural world.
Similarly, advances in medical science have led to a greater understanding of the human body and the treatment of diseases, which has influenced our values around health and well-being.
Questions and Answers
What is the purpose of science a to z puzzle answers?
Science a to z puzzle answers aims to provide a comprehensive and engaging resource for anyone seeking to expand their scientific knowledge.
How is the information organized?
The information is meticulously organized into various categories, including definitions, experiments, discoveries, applications, and more, ensuring ease of navigation and exploration.
Is this resource suitable for all ages?
Absolutely! Science a to z puzzle answers is designed to cater to individuals of all ages, from curious children to lifelong learners.